A comparatively new ransomware operation known as Interlock assaults organizations around the globe, taking the bizarre method of making an encryptor concentrating on FreeBSD servers.
Launched in late September 2024, Interlock has claimed duty for assaults towards six organizations and posted stolen knowledge on its knowledge breach website after a ransom was not paid. One of many victims is Wayne County, Michigan, which suffered a cyber assault in early October.
Not a lot is thought concerning the ransomware operation, and a few of the first info got here from incident responder Simo in early October. who discovered a brand new rear door (VirusTotal) deployed in an Interlock ransomware incident.
Shortly after, the cybersecurity researcher MalwareHuntTeam discovered what was believed to be a Linux ELF cipher (VirusTotal) for interlock operation. Sharing the pattern with BleepingComputer, we tried testing it on a digital machine, the place it instantly failed.
Examination of the strings throughout the executable indicated that it was compiled particularly for FreeBSD, and the Linux “File” command additional confirmed that it was compiled on FreeBSD 10.4.
interlock.elf: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, model 1 (SYSV), statically linked, BuildID(sha1)=c7f876806bf4d3ccafbf2252e77c2a7546c301e6, for FreeBSD 10.4, FreeBSD-style, not stripped
Nonetheless, even when testing the pattern on a FreeBSD digital machine, BleepingComputer was unable to run the pattern appropriately.
Whereas it is not uncommon to see Linux ciphers constructed for VMware ESXi servers and digital machines, it’s uncommon to see some constructed for FreeBSD. The one different ransomware operation identified to have created FreeBSD encryptors is Hive ransomware operation now defunctwhat was discontinued by the FBI in 2023.
This week, researchers from cybersecurity agency Development Micro shared on X that they discovered a further pattern of FreeBSD’s ELF encryption (VirusTotal) and a pattern Home windows encryption operation (VirusTotal).
Development Micro additional mentioned that the menace actors possible created a FreeBSD encryptor, because the working system is often utilized in important infrastructure, the place assaults may cause widespread outages.
“Interlock targets FreeBSD as a result of it’s extensively utilized in servers and important infrastructure. Attackers can disrupt important providers, demand giant ransoms, and power victims to pay,” explains Development Micro.
Interlock ransomware
Whereas BleepingComputer could not get the FreeBSD encryptor to work, the Home windows model ran with out concern on our digital machine.
In accordance with Development Micro, Home windows Encryptor will clear Home windows occasion logs and, if automated elimination is enabled, will use a DLL to take away the principle binary utilizing rundll32.exe.
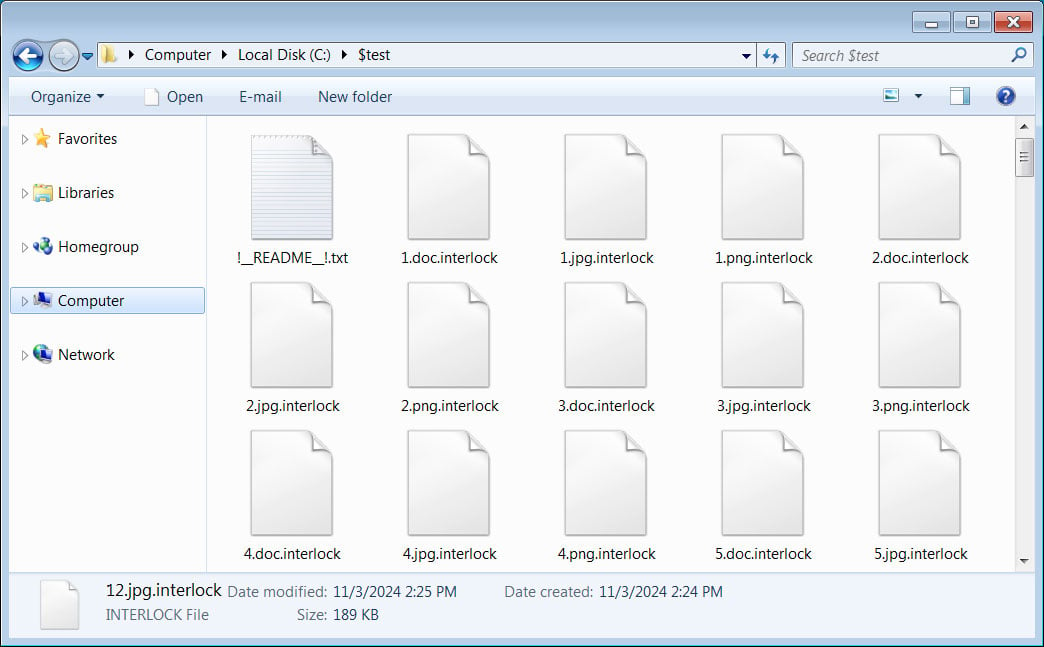
By encrypting recordsdata, the ransomware will add the .weave extension to all encrypted file names and create a ransom observe in every folder.
Supply: BleepingComputer
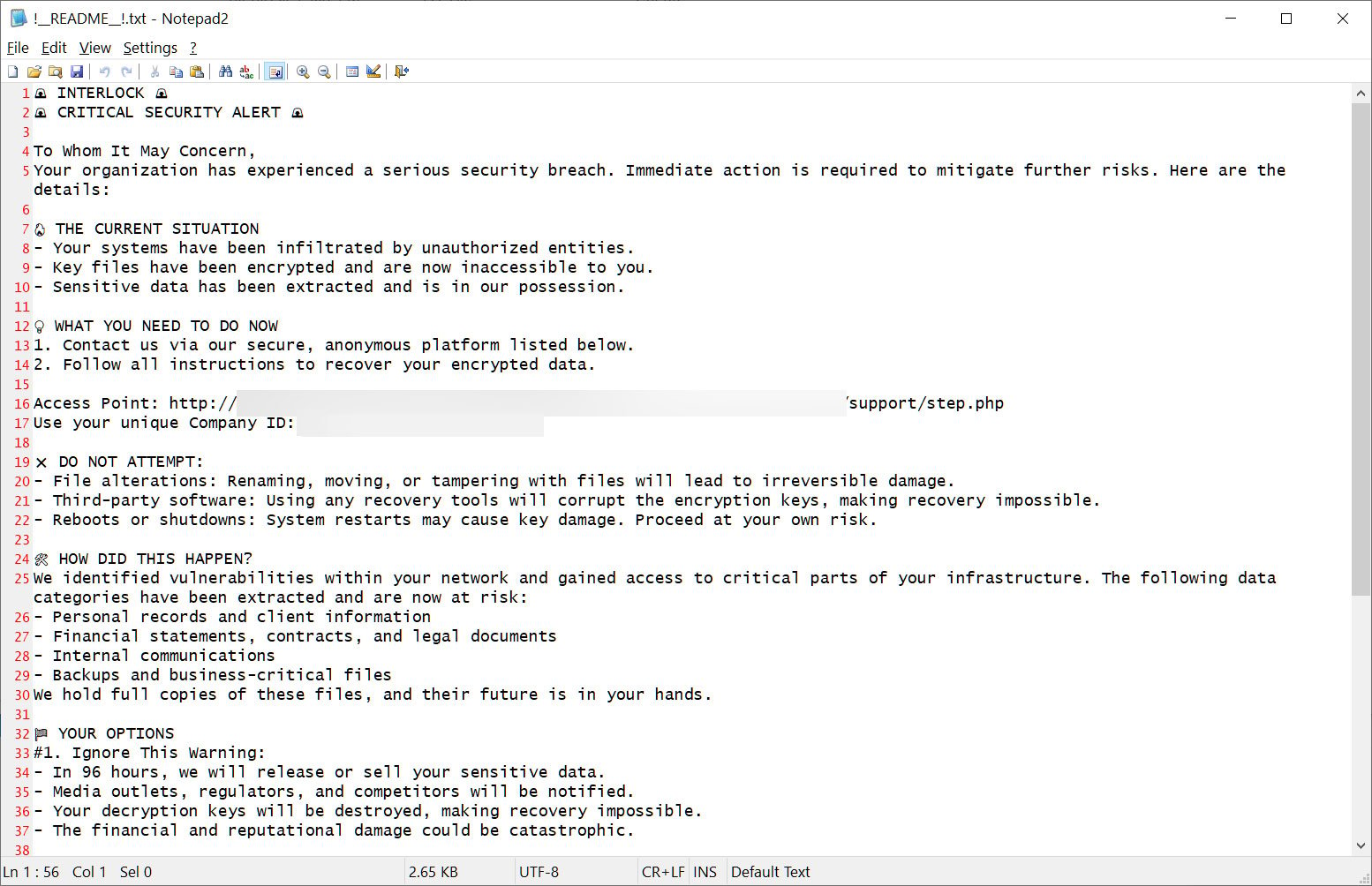
This ransom observe is named !__README__!.txt and briefly describes what occurred to the sufferer’s recordsdata, makes threats and hyperlinks to Tor buying and selling websites and knowledge leaks.
Supply: BleepingComputer
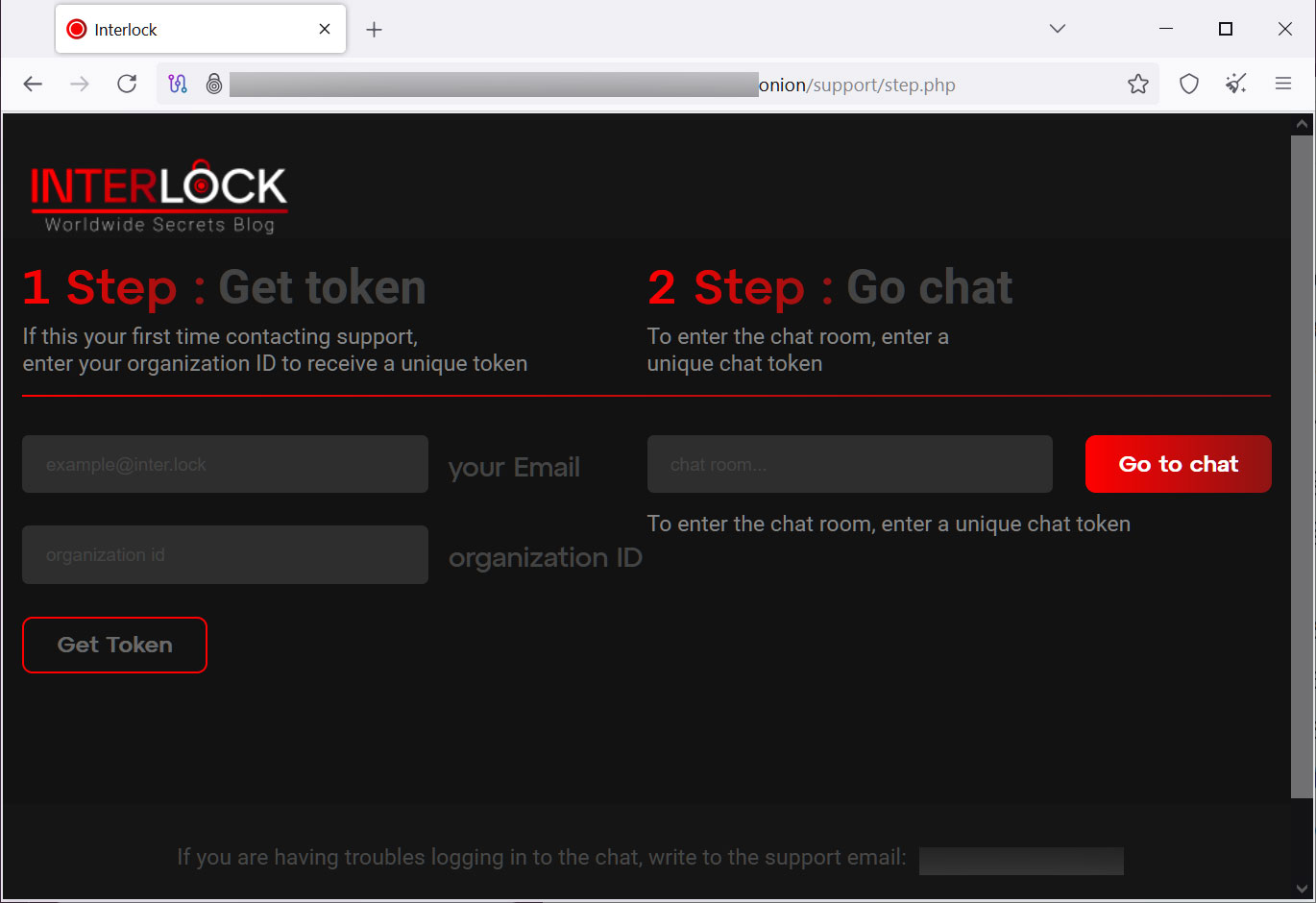
Every sufferer has a singular “Firm ID” that’s used together with an electronic mail handle to register on the menace actor’s Tor buying and selling website. Like many different latest ransomware operations, the victim-targeted buying and selling website solely features a chat system that can be utilized to speak with menace actors.
Supply: BleepingComputer
When finishing up assaults, Interlock will breach a company community and steal knowledge from servers whereas spreading laterally to different gadgets. When completed, the menace actors deploy the ransomware to encrypt all recordsdata on the community.
The stolen knowledge is used as a part of a double extortion assault, during which the menace actors threaten to leak it publicly if the ransom will not be paid.
Supply: BleepingComputer
BleepingComputer has discovered that the ransomware operation calls for ransoms starting from tons of of hundreds of {dollars} to thousands and thousands, relying on the dimensions of the group.

