GitHub has an issue with inauthentic “stars” getting used to artificially inflate the recognition of malware and rip-off distribution repositories, serving to them attain extra unsuspecting customers.
Stars are much like “Like” buttons on social media websites, permitting GitHub customers to favourite a repository. GitHub makes use of stars as a part of an general score system and to indicate you associated content material it thinks you would possibly like.
“You may star repositories and subjects to find related tasks on GitHub. If you star repositories or subjects, GitHub can advocate associated content material in your private dashboard,” he explains GitHub.

The problem has been documented earlier than, comparable to final summer time when Examine Level found a malware supply service referred to as ‘Stargazers Ghost Community,’ which used an intensive community of inauthentic customers working faux tasks to push data-stealing malware.
Non-malicious tasks additionally use faux stars to extend their recognition, enhance their attain, and entice the eye of reputable customers, actual stars, and adoption.
TO new examine carried out by researchers at Socket, Carnegie Mellon College, and North Carolina State College offers us a greater thought of the magnitude of the issue, discovering 4.5 million stars on GitHub which can be suspected to be faux.
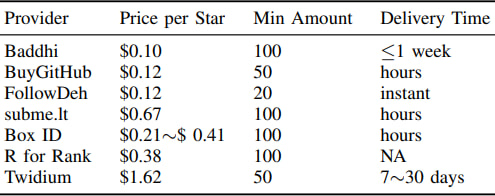
Supply: Arxiv.org
Looking for faux stars
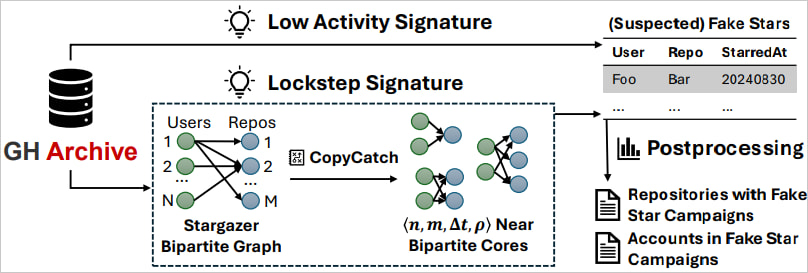
The researchers developed and used a software referred to as ‘StarScout’ to research 20 TB of ‘GHArchive’ knowledge to seek out non-genuine stars.
GHArchive accommodates metadata for greater than 6 billion GitHub occasions from July 2019 to October 2024, together with 60.5 million consumer actions throughout 310 million repositories and 610 million stars.
StarScout detects customers who present minimal exercise on GitHub, comparable to highlighting a single repository, having bots or momentary account exercise patterns, and teams of accounts performing in coordination, comparable to highlighting the identical repositories in a short while.
Their methodology relies on CopyCatch, an algorithm designed to detect fraudulent patterns on social networks.
Supply: Arxiv.org
4.5 million stars suspected of being faux
After processing the info by making use of low-activity and synchronized signature algorithms to establish suspicious stars within the repositories, the workforce discovered 4,530,000 inauthentic suspicious stars offered by 1,320,000 accounts in 22,915 repositories.
To extend confidence within the true nature of those stars, the researchers filtered out attainable false positives by contemplating solely repositories with a big anomalous peak of stellar exercise in a single month, and for which the proportion of falsifications exceeded 10%, in contrast with the whole variety of stars.
This decreased the outcome to three,100,000 faux stars awarded by 278,000 accounts in 15,835 repositories.
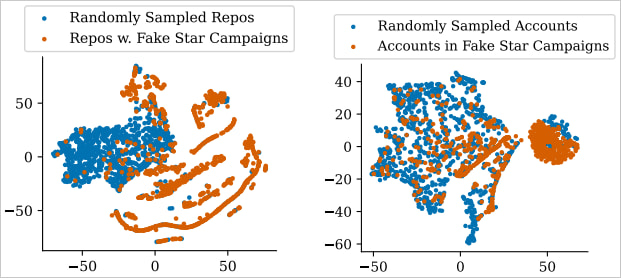
Supply: Arxiv.org
Of those, roughly 91% of repositories and 62% of accounts suspected of being unauthentic had been eliminated by October 2024, supporting the accuracy of the StarScout software.
The examine additionally reveals that faux star exercise elevated in 2024, with roughly 15.8% of repositories that had greater than 50 stars in July 2024 concerned in these malicious campaigns.
Researchers reported that the repositories and accounts StarScout recognized as inauthentic in July 2024 and GitHub eliminated all of them. Nonetheless, they’re nonetheless within the means of evaluating and reporting on extra clusters present in November 2024.

Supply: Arxiv.org
The implications of pretend stars on GitHub and its customers are manifold, however general, the problem erodes belief within the platform and the varied software program tasks hosted on it.
Customers ought to look past the celebs, consider the exercise and high quality of the repository, learn the documentation, study the content material and contributions, and evaluate the code if attainable.
GitHub’s deceptive repositories are widespreadand the platform has even been exploited in state-sponsored operations, so watch out when downloading software program from it.
BleepingComputer has reached out to GitHub for extra data on how the platform is actively preventing the faux stars challenge, however we’re nonetheless ready for his or her response.

